
Social distancing rules and lockdowns during the coronavirus pandemic had a “catastrophic” and “devastating” impact on Britain’s arts, culture and heritage organisations, with output falling by 60% over the past 18 months.
That’s the finding of a major new report by researchers at the University of Sheffield which analysed how COVID-19 has affected museums, galleries, cinemas, theatres and other arts and cultural organisations.
As the pandemic took hold in March 2020, the impact on the sector was immediate. Annual gross valued added (GVA) output fell dramatically with a decline of around a third from the second quarter of 2019 to the same period last year in real terms.
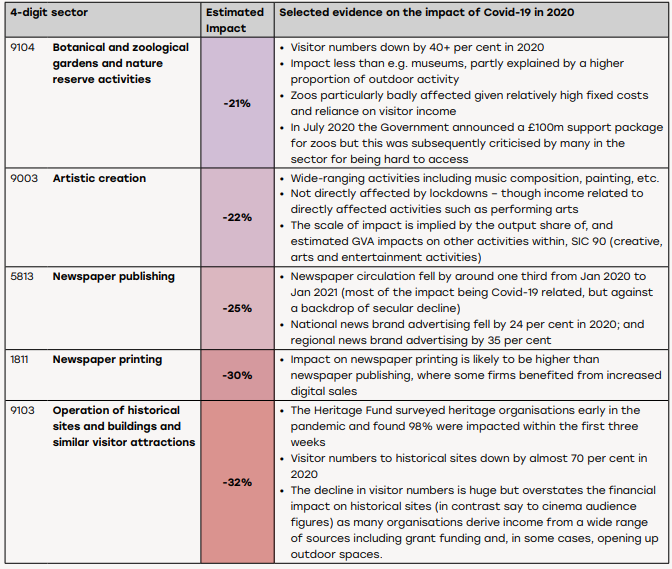
Businesses categorised as “creative, arts and entertainment activities” along with libraries, archives and museums were worst hit with declines of 63% and 45% respectively.
Few businesses saw an increase although with millions of people locked down at home and looking for entertainment, computer games companies experienced a 18% rise in output, while book publishing firms increased output by 2%.
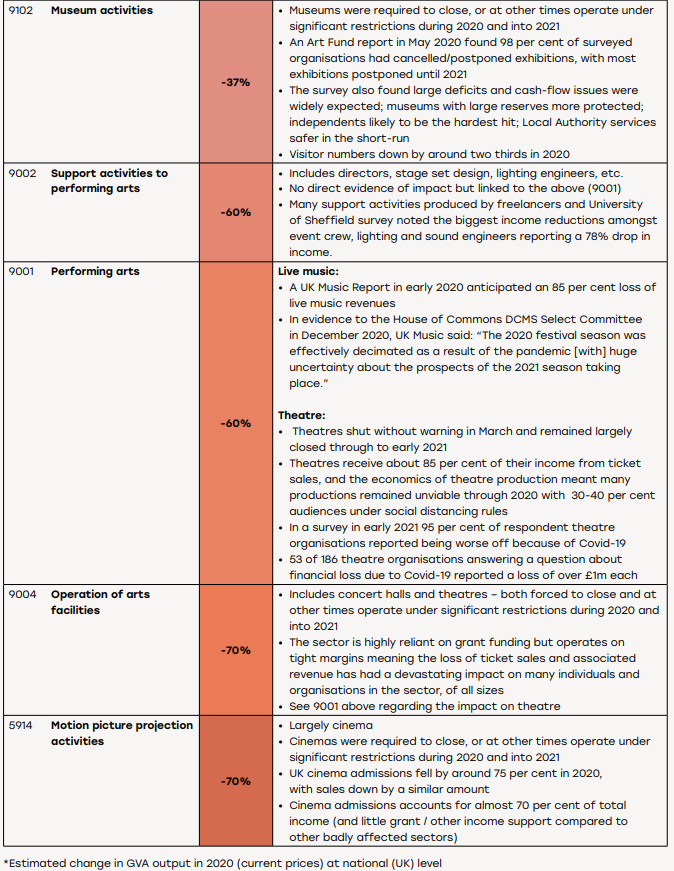
At the other end of the scale, with theatres shuttered during lockdown and then facing limits on audiences, output among performing arts organisations declined 60%, while it fell 70% at cinemas.
Government funding has been vital for the survival of arts, culture and heritage businesses during the pandemic. The study found that 55% of employees in the sector were furloughed through the Coronavirus Job Retention Scheme. That’s the second highest sector behind accommodation and food.
At its peak in May 2020, 450,000 arts, entertainment and recreation employees were furloughed, falling to 150,000 by the end of May 2021.
Freelancers were hard hit too, given the high number employed by arts and culture organisations. They made more than 80,000 claims for grants through the Self-Employment Income Support Scheme (SEISS), 68% of the UK’s eligible population.
The funding was not without its problems though. For the fourth round of SEISS, 181,000 self-employed people in the arts sector were assessed for eligibility, the research revealed, but only 54% were deemed eligible – compared to 67% across all sectors.
“There is substantial evidence to suggest that a large number of people in the sector failed to claim under either the SEISS scheme or the furlough scheme, due to their strict eligibility criteria,” the report said.
“Many creatives move between employment and self-employment or do both at the same time – a reflection of the dynamism of the sector – meaning they’ve not qualified for either SEISS
or furlough, or only been able to claim small amounts of support.
“Others have their own companies for work purposes which were seen to fall between the two schemes. In short, there has been insufficient support for a large number of self-employed people in the CAH sector.”
Please respond to our new survey about the creative industries in Bristol and Bath. It will help us design – and advocate for – future support for the creative economy in our region.
The £1.5bn Cultural Recovery Fund (CRF) was another vital scheme. It was set up by the Department for Culture, Media and Sport in July 2020 in response to data gathered during the first lockdown which suggested 65% of arts and culture organisations had stopped trading and over 30% would run out of cash by September 2020.
The University of Sheffield report said the success rate of applicants for revenue grants was 69% and 70% for capital grants.
The amount of funding received through CRF varied between regions but the study said it “includes a handful of very large grants/loans which distorts the overall picture”.
Among those areas was Gloucestershire, Wiltshire and Bath/Bristol due to a £23m loan to English Heritage based in Swindon and a £6m capital grant to Bristol Beacon (formerly Colston Hall) which is currently undergoing refurbishment.
The report also highlighted some local authority schemes set up to help creative businesses deal with the impact of the pandemic. The examples cited include the West of England Combined Authority’s Creative Sector Growth Programme. Find details in our creative industries funding guide.
The report includes a specific focus on the experiences during the pandemic of freelancers in the arts and culture sector in South Yorkshire. The findings are likely to ring true for thousands of other self-employed people in other parts of the UK.
More than three quarters of freelancers said their mental wellbeing was worse since the start of lockdown. Male respondents, under-30s, and those with a diagnosed mental health condition experienced even greater levels of distress.
The main causes of stress and worry were personal finances, unemployment and the ability to cover overheads. Anxiety over these issues was much higher amongst freelancers than the general population.
South Yorkshire freelancers also reported lower levels of wellbeing and happiness and higher levels of anxiety than the general public. With their mental health impacted, the report said the pandemic led “to a sense of lost identity, skills and motivation”.
Event crew, lighting and sound engineers reported greater worsening of mental health than respondents in other roles, with 53.8% saying that their mental health was “much worse” compared to 25.5% on average.
Professor Vanessa Toulmin, director of city and culture and chair in early film and popular Entertainment at the University of Sheffield, said:
“The COVID-19 pandemic has had a devastating impact on the UK’s arts, culture and heritage sector. This landmark report reveals how social distancing and lockdowns over the past 18 months have had a catastrophic effect on the finances of people who work in the sector, as well as businesses and venues.
“People have lost their jobs, businesses and venues have closed and this economic impact has severely affected the mental health and wellbeing of people who work in the sector across the UK. People in the sector have been losing sleep and have had much higher levels of anxiety due to how the pandemic has affected their personal finances and uncertainty about the future.”
The creative industries contribute to making Bristol and Bath amazing places to live and work. But how can they grow and prosper? Tell us in our survey here.
Bristol Creative Industries is the membership network that supports the region's creative sector to learn, grow and connect, driven by the common belief that we can achieve more collectively than alone.